There are 35 decentralized exchanges created on various blockchains, and the industry is quickly expanding. For example, Uniswap, which is on the Ethereum blockchain, has the highest trade volume of any DEX. Historically, centralized players dominated this field. However, as the available technology stack evolves quickly, an increasing variety of tools enabling decentralized transactions have developed. As a result, the future of cryptocurrency exchanges appears to be slowly but gradually turning toward decentralized exchanges. It can one day replace our centralized exchanges. In this article, we will get a complete understanding of Decentralized Exchanges.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Decentralized Exchanges
A Decentralized Exchange is a platform where users may trade cryptocurrencies without the use of an intermediary.
- Middlemen: They do not use an intermediary entity to settle transactions, instead of relying on self-executing smart contracts to facilitate trade. This allows for quick trades, typically at a lesser cost than on centralized cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Custody: They adopt a non-custodial architecture in the absence of intermediaries. This means we keep ownership of our cryptocurrency and manage our wallets and private keys. Thus, we have total control over our funds.
- Risk: As there is no intermediary, most DEXs have little counterparty risk and are not obliged to follow Know-Your-Customer (KYC) or Anti-Money-Laundering (AML) regulatory norms.
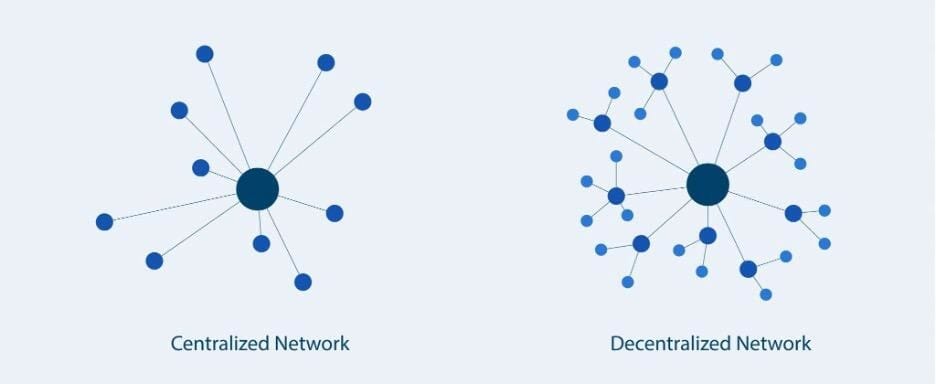
Implementations of Decentralized Exchanges
What are Order Books?
Order books keep track of all open buy and sell orders for a specific asset. The difference between these values defines the depth of the order book and the current market price. This information is commonly stored on-chain during trades on DEXs with order books, while our funds stay off-chain in our wallets. This is the initial phase of decentralized exchanges, like traditional centralized exchanges, which use order books.
What are Major Decentralized Projects?
dYdX
- It is a non-custodial decentralized exchange to create open, safe, and strong financial products.
- It also allows peer-to-peer lending, allowing us to generate passive income while our assets are kept on the exchange.
- It is built on Ethereum smart contracts.
- It blends decentralized exchange security and transparency with centralized exchange speed and usability.
Loopring
- This platform includes an order-book-based DEX protocol called zk-Rollups, which validates transactions with zk-SNARKs technology.
- It’s objective is to combine centralized order matching with decentralized on-blockchain order settlement to create a hybridized solution that incorporates the best features of both centralized and decentralized exchanges.
Swaps
The next generation of decentralized exchanges will use liquidity pool protocols to decide asset prices.
UniSwap
- It is an interface for exchanging ERC20 tokens, which is built on Ethereum.
- It is dedicated to enabling free and decentralized asset exchange by serving as an open-source frontend interface for traders and liquidity providers.
- It intends to provide token trading automated and available to anybody who has tokens.
- To learn more, read our guide to Uniswap.
SushiSwap
- It is a fork of Uniswap.
- The trading cost on Uniswap is 0.3 percent; however, SushiSwap divides the 0.3 percent differently, distributing 0.05 percent in the form of SUSHI tokens.
- It also wants to add extra features which were not previously present on Uniswap.
To learn more about Swap platforms, read Best Crypto Swap Platforms.
Aggregators
- Decentralized exchanges employ a variety of protocols and processes, resulting in a lack of liquidity.
- To solve this, the third generation of DEXs, known as aggregators, have created tools to expand asset liquidity pools across centralized and decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges.
1inch
- It is a DEX aggregator that connects many DEXes into a single platform, allowing users to locate the most economical exchanging routes across all platforms.
- To learn more, our guide to 1inch.
DeversiFi
- To enhance liquidity, this protocol combines liquidity across both centralized and decentralized exchanges.
- It also takes advantage of StarkWare’s batching technology to settle 9,000+ trades per second via user interface or API.

Working of Decentralized Exchanges platforms
On-Chain Order Books
- Here everything is done on-chain. Every order is recorded on the blockchain. We are not relying on a third party to convey orders to us.
- Fees: We pay fee since we ask every node on the network to record the order forever. We must wait until a miner adds our transaction to the blockchain.
- Flaw: Front running is the flaw in this method. It happens when an insider is aware of a pending transaction and uses that knowledge to execute a trade before the transaction is processed.
- Although it is no possible to front run as everything is recorded on a global ledger. However, there is another type of attack where a miner sees the order before it is verified and guarantees that their own order is put to the blockchain first.
Stellar
- It is an open network that allows funds to be transferred and stored.
- Lumens, the network’s native token, acts as a bridge, making it less expensive to transfer assets across borders.
- This aims to challenge existing payment providers that provide a comparable service at high costs.
- You can also invest in Stellar by buying its utility token called XLM. Read our guide to buy XLM to learn more.

Bitshares
- It is a decentralized platform used for safely exchanging cryptocurrencies without intermediaries.
- It is based on the open-source blockchain technology Graphene, which is said to be capable of processing up to 100,000 transactions per second (TPS), making it quicker than MasterCard and VISA combined.
Off-Chain Order Books
- Centralization: Off-chain DEXs are more centralized than on-chain. Instead of being uploaded to the blockchain, each order is hosted elsewhere.
- Flaw: The order book might be managed entirely by a centralized body. If that entity is malicious, they can manipulate the markets to some extent, i.e., by front running or misrepresenting orders.
- 0x protocol: It deployed on the Ethereum blockchain. It provides a framework for relayers to maintain off-chain order books. Trade is only completed after both parties are matched.
- Speed: They do not suffer the same speed restrictions since they do not use as much blockchain.
Binance
- It is the world’s largest centralized cryptocurrency exchange.
- It allows users to trade cryptocurrencies online.
- It supports the majority of the most widely traded cryptocurrencies.
- It offers a crypto wallet in which traders may keep their funds.
The exchange also provides customers with services that allow them to earn interest or trade with cryptocurrency. It also provides programs that assist miners and dealers make financial decisions.
Read our Binance Review to know more.
0x Protocol
- It is an infrastructure protocol that enables users to trade ERC20 tokens and other assets on the Ethereum blockchain without intermediaries.
- It provides this decentralized exchange capability by using a set of open-source, publicly auditable smart contracts that collaborate to create a flexible, low-friction trading protocol that developers can incorporate into their products.
Automated Market Makers
- Here, the order book is replaced by liquidity pools.
- Users supply the liquidity by becoming liquidity providers, and they receive passive income on their deposits through trading fees based on the percentage of the liquidity pool they offer.
Kyber Network
- It is a hub of liquidity protocols that combine liquidity from many sources to ensure safe and quick transactions in all decentralized applications.
- Here, transactions are on-chain so that any Ethereum Block Explorer can check quickly.
- It aims to resolve the liquidity problem in the DeFi business by enabling developers to construct goods and services without worrying about liquidity.
Balancer
- It was built on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Its protocol acts as a weighted portfolio, price sensor, and liquidity provider self-balancing.
- It lets users earn profit using its $BAL token by contributing to customizable liquidity pools.
How to choose Decentralized Exchanges?
In this section, we will understand how to choose DEX and the points one should keep in mind.
- Audit History: Ensure that the DEX has been subjected to several rigorous audits before its launch.
- Volume: DEXs with the Volume of over 30 days are trustworthy.
- Community: Check whether DEX has a sizable community behind it and that they are active on social media platforms such as Twitter.
- Other Factors: KYC Requirements, Liquidity, Trading Costs, and supported tokens should all be considered.
Advantages of Decentralized Exchanges
Anonymity
- CEX: To comply with customer’s KYC standards, all centralized exchanges requests require sign-up. This requires the owners of cryptocurrencies to provide the exchange provider with their data.
- DEX: This is not carried out by most DEXs. Since no central body maintains them, KYC standards are not necessary. This provides privacy for users while they trade on DEXs. We only need our public address needs decentralized exchanges.
Security
- CEX: Breaches of the Security of centralized exchanges like as Coincheck, Mt. Gox and Bitfinex shattered and severely damaged the public’s trust. A loss of 530 million dollars of cryptocurrencies came from the Coincheck theft, which broke the previous record for MtGax of 472 million dollars. CEXes preserve their liquidity by keeping their user’s funds on the platform, making them vulnerable to large-scale theft.
- DEX: Here, users are responsible for keeping their accounts secure. The robbery of funds from individual users would be unprofitable for hackers since it might be too complex and costly.
Sovereignty
- CEX: Here, users do not have complete custody and can utilize their funds at their will.
- DEX: Here, users will have complete custody and can utilize their funds at their will.
Downtime
- CEX: There are maintenance breaks.
- DEX: They do not have a single failure point, which means that the rest of the DEX nodes will keep it up and operate, even when a node or many nodes are offline due to attacking or maintenance. This dramatically lowers the exchange downtimes and facilitates the roll-out of upgrades.
Fees
- CEX: They charge high fees as compared to DEXes.
- DEX: It requires relatively little maintenance fees. They need money to support themselves; however, a small fee is collected each time a user performs a transaction.
Adoption of New Assets
- CEX: They charge a fee for listing new cryptocurrencies.
- DEX: There is no listing fees in this case.
Disadvantages of Decentralized Exchanges
Fiat
- CEX: They can work with Fiat as we can easily convert our Fiat to crypto from them.
- DEX: They only work with cryptocurrency assets and not Fiat, as enabling crypto-to-fiat would require involvement with banks.
Customer Service
- CEX: Centralized exchanges like banks. It has clients that they wish to keep satisfied most of the time. Therefore they have high-quality customer support.
- DEX: But this is not with the case of the decentralized exchange. The protocol creators have no connection with users. So there is no customers support.
Complexity
- CEX: Mostly, all types of trades are possible.
- DEX: Uniswap and many other DEXs are built on the Ethereum blockchain. All exchanged tokens must be on the Ethereum blockchain. So Bitcoin and many other famous blockchains tokens cannot be used here.
Liquidity
- CEX: CEXes generate Liquidity by their huge capital.
- DEX: Their Liquidity depends significantly on the amount of users actively trading on the platform. However, they have come up with a solution utilizing liquidity pools.
Conclusion
Even though centralized exchanges account for the vast majority of market activity because they provide security, regulatory supervision, and even insurance, the emergence of DeFi has opened space for the creation of decentralized crypto exchange protocols and aggregation tools. Decentralized exchanges usually strive to represent the blockchain concept of trustlessness and anonymity. For example, Ethereum-based DEXs have experienced a significant increase in usage due to the emergence of DeFi. In addition, Uniswap, Curve, and Balancer demonstrate the possibility of simple, user-friendly platforms that rely on liquidity protocols rather than order books.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do DEXes Suffer from Downtime?
Can we convert our Crypto to Fiat in DEXes?
If DEXes are Better than CEXes, then why do people use CEXes then?
Are there any middlemen in DEXes?
Are our funds secured in DEXes?
Also, read