Most people know that Blockchain Technology is an immutable, secure, unhackable decentralized network. But how come this technology is so robust and can stand out from all the present Technologies. In this article, I will give you a clear picture of Blockchain architecture, which made Blockchain Technology stand-out from other technologies.
In this article we will see
- Centralized Database v/s Decentralized database
- What is Blockchain Architecture?
- How Does It Work?
- What is Consensus Mechanism?
- Different types of Blockchain Architecture?
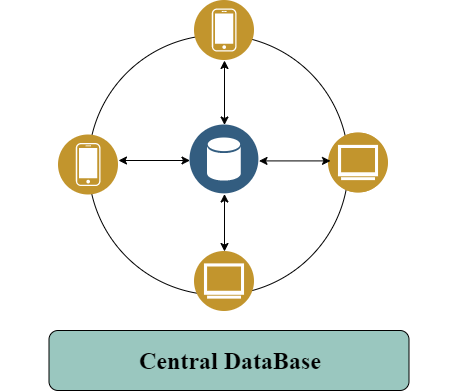
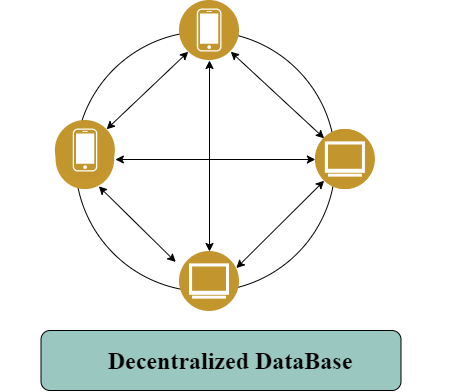
Centralized Database v/s Decentralized database
The data which is stored in a single location is called the centralized database. The decentralized database is totally different from the centralized database. Every Node or User who is in the system holds the full data which is present in the system.
- If the centralized system fails, then the entire system is halted. But, in the decentralized DB, there will be no problem because every node in the system holds the data.
- Decentralized DB is more reliable and reactive than centralized DB.
- Decentralized DB is more sophisticated than centralized DB.
For more understanding, I have created a visualization of this process.
What is Blockchain Architecture?
We know that Blockchain technology is a decentralized distributed ledger with a chain of blocks.
We will see what exactly these blocks contain and how these blocks help us making data immutable and secure.
Every Block consists of Block Header, Hash of Previous Block Header, Merkle root of the transaction. All these blocks are connected to the following block with the help of the pointer (like a LinkedList).
For more understanding, I have created a visualization of this process.
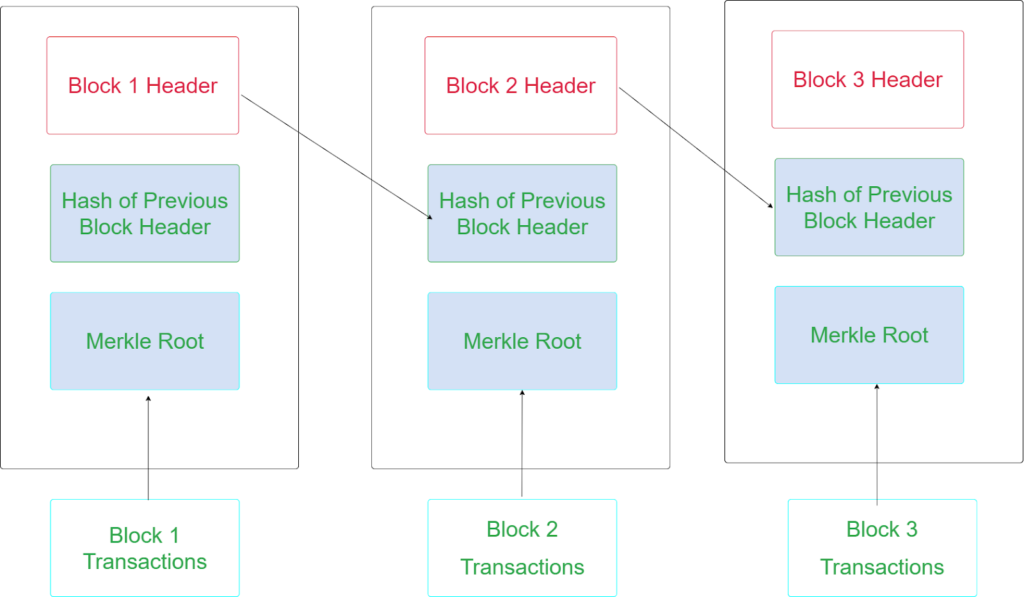
Block Header
Block Header is the core part of the Block, which is the main way to identify the block in the blockchain. Let’s see what data the block header holds in the block.
The block header data is shown in the table below

Previous Block Hash: The Block Hash of the block that this block is being built on top of. This is what “chains” the blocks together.
Timestamp: When the miner is mine this block, the Unix timestamp at which this block header is being hashed is noted within the block header itself.
Merkle Tree: All of the transactions in this block, hashed together. Basically provides a single-line summary of all the transactions in this block.
Difficulty Target : The difficulty target for the block.
Nonce: The field that miners change in order to try and get the target hash of the block header (a Block Hash).
How Does It Work?
These are the core blockchain architecture components:
Node – Any computer or machine, which holds the complete copy of the blockchain ledger.
Transaction – Every data or information which we store on the block change is in the form of transactions.
Block – Block consists of Block Header, Hash of Previous Block Header, Merkle root of the transaction.
Chain – Sequence of blocks in a specific order.
Miners – The nodes who produce a block and perform the block verification process before adding anything to the blockchain structure. Miners will compete with each other to solve the puzzle to earn rewards.
Consensus (consensus protocol) – Consensus is a way of reaching an agreement in a group. Where a set of rules and arrangements to carry out blockchain operations. Any transaction within the blockchain should follow the rules and arrangement of Consensus.
I have created a visualization of the Blockchain Architecture diagram that shows how this actually works
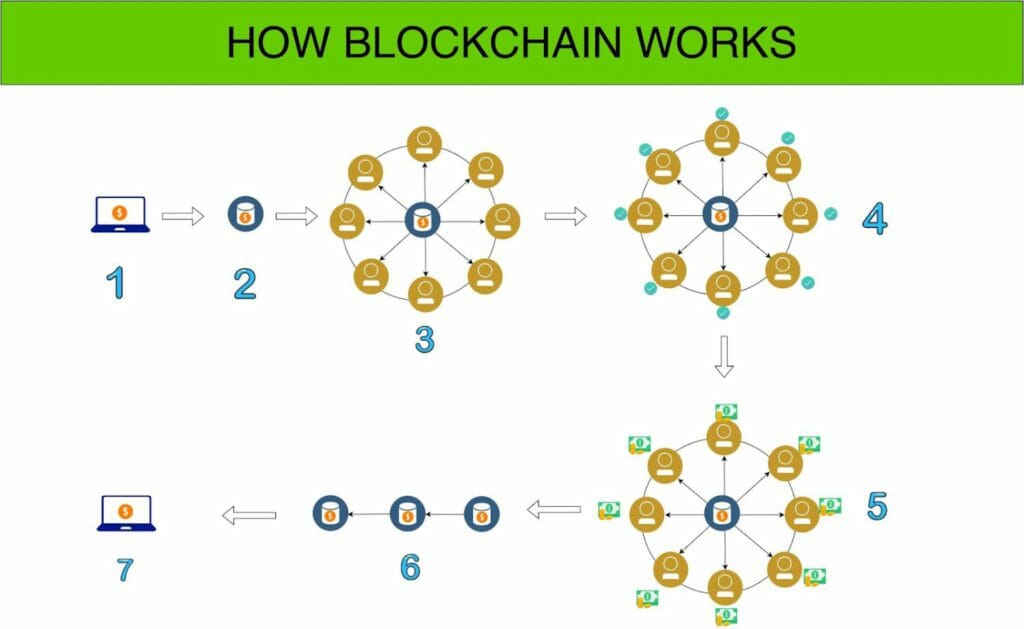
- Transaction is Initiated.
- The Transaction is placed in a Block.
- The block of a transaction is sent to every node in the network.
- Miners validate the transaction using consensus mechanism Proof of Work
- Miners who successfully crack the puzzle in “Proof of Work” will receive the reward.
- The Block is now successfully placed on the existing Blockchain.
- The transaction is Successfully Completed.
What is Consensus?
In simple terms, the Consensus is a way of reaching an agreement in a group. While voting just settles for a majority rule. A consensus, on the other hand, makes sure that an agreement is reached which could benefit the entire group as a whole.
“From a more idealistic point-of-view, Consensus can be used by a group of people scattered around the world to create a more equal and fair society.”
A method by which consensus decision-making is achieved is called “consensus mechanism”.
For more information on Consensus Mechanism.
Different types of Blockchain Architecture?
- Public Blockchain / Permissionless Blockchain
- Private Blockchain / Permissioned Blockchain
- Consortium Blockchain / Permissioned Blockchain
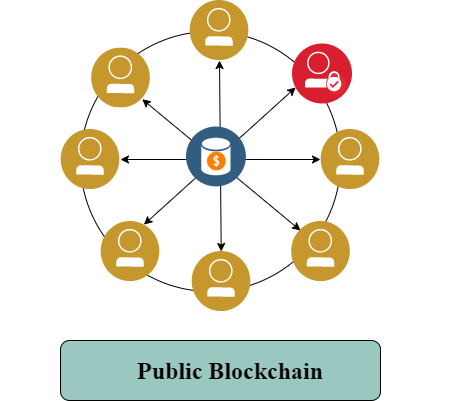
Public Blockchain
A Public blockchain means that anyone can have access to the blockchain without anyone’s permission. That’s why these blockchains are also called permissionless blockchains. Ethereum and Bitcoin are examples of public blockchains.
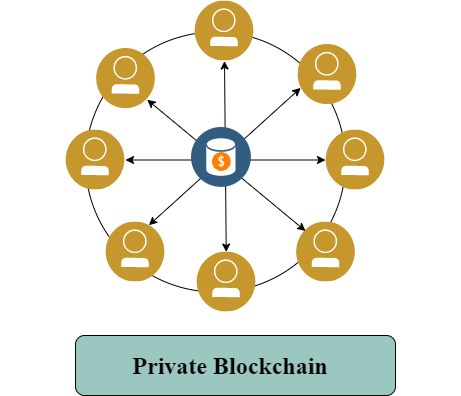
Private Blockchain Architecture
A private blockchain is opposite to public blockchain. It is controlled by an organization or entity. Therefore, the entity in control decides the participants of the network. That’s why private blockchains also called permissioned blockchains.
Also Read: Permissionless Blockchain vs Permissioned Blockchain
Consortium Blockchain Architecture
Consists of multiple groups/entities and controlled by a specially assigned node. We have created a visualization of the public blockchain and private blockchain.
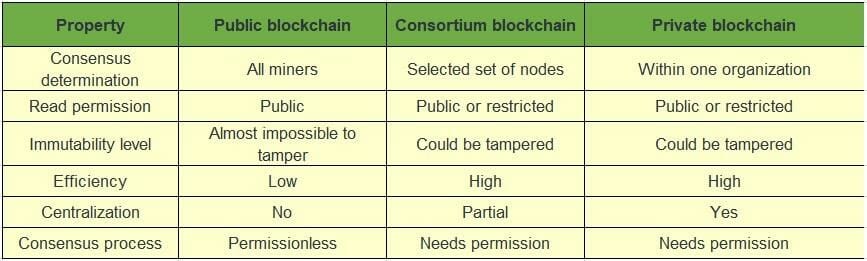
Comparison of Public v/s Consortium v/s Private Blockchain
Conclusion
We now know why blockchain technology is known as ROBUST technology and how it stands out from other technologies. There are many use cases of blockchain technologies and entrepreneurs are building a new more transparent future using this technology. You can discover new blockchain products on CoinCodeCap every day.
Attribution
This article is contributed by B Shiva Sai Kumar.