Before understanding Polygon (MATIC), Ethereum has brought many advancements into cryptocurrency, over the years, including smart contracts and high-interest-paying decentralized applications.
However, it faces three significant challenges. The first is the Low Throughput issue, which means Ethereum can only handle 30 transactions per second. This processing speed is considerably low for the number of people using Ethereum. Since many alternatives can process more transactions in the same time frame. For example, the Cardano blockchain does around 257 transactions per second, while Polkadot can do up to 1000 TPS, and Solana can do up to 65000 TPS.
The second big problem is that the Ethereum network could be more user-friendly. In short, this means it is expensive. Lastly, the Ethereum blockchain presents developers with limited options. All Ethereum projects run on the same network and they all have similar Throughput. This implies that they all share Ethereum’s problems with no exceptions. But what if there was another blockchain that leveraged Ethereum’s technology while also offering higher Throughput, extremely low transaction fees, and better options? In this article, we have explained what a Polygon is, how it works, and the specific Tokenomics of the Matic coin.
In 2016, three Indian Developers sought to find a solution to Ethereum’s problems, which resulted in the creation of Matic, now the Polygon network, the coin is called the Matic coin.
What is Polygon (MATIC) ?
Polygon (MATIC) is a layer-two scaling platform allowing Ethereum-based applications to tackle the problems mentioned above regarding Ethereum. While also leveraging Ethereum’s security, its primary focus is to increase the usage of DeFi tools and applications. By basically connecting blockchains, the network currently hosts over 3000 decentralized applications, of which over 80 big names migrated from the Ethereum main chain.
Since Polygon is similar to Ethereum, many creators that develop useful tools will shift them from Ethereum to other EVM blockchains like Polygon. That way, they can increase their reach and usage. EVM stands for Ethereum Virtual Machine, and it’s the code run by computers worldwide to carry out the blockchain’s smart contracts.
Polygon has an EVM, but so does the Binance Smart chain, Fantom, and other big networks. They all utilize the main Ethereum code. And since they run all the same code, it makes sense that developers can move their projects over to a new network. And it’ll work the same way without making many changes.
Polygon Proof of Stake
Most people think about the Polygon proof of stake chain, which is simply a side chain to Ethereum, utilising a proof of stake consensus mechanism. There’s a few other changes to this side-chain, but what’s really important is that it’s way faster and can handle way more transactions per second. Also meaning it’s much more affordable to the end user.
The Polygon network is lot more than just a side chain. One of the core ideas behind Polygon is to equip developers with user friendly and flexible tools that way they can fast track Ethereum’s transformation into a multi chain platform. To put this in simpler words Polygon isn’t just a single proof of stake chain. They are a series of blockchains that can help scale Ethereum.
Developers can easily create all kinds of different scaling solutions that they can use with Ethereum like completely seperate chains like Zk Rollup chains Optimistic Rollup chains, or any other side chains that they desire.
Side chains and rollups are unique and creative way to bundle up data and save space on the main Ethereum chain. The Polygon proof of stake chain is just one way to scale Ethereum. In reality, Polygon plans to create many different solutions for users to scale it. Polygon is pretty simple but when you look at it’s internals, there’s lot more than what regular users see.
In easy words Polygon basically Ethereum but with super cheap gas fees. Right now, to transfer your Ethereum from one account to another, The fee is like 20 dollars. However, on the Polygon network, it is less than a penny. This means, users are free to try out new apps and test things out without the fear of losing a 150 dollars over a token swap.
Also, you may read: A Deep Dive Into Solana: SOL Tokenomics Explained
How Does Polygon Work?
Polygon is driven by the layer-2 scaling solution and the proof of stake protocol serving as a committed chain to the main Ethereum chain. The commit chain functions as a transaction network that operates close to the real chain. Therefore, in Polygon’s case, it works alongside Ethereum.
The Polygon commit chain groups up clusters of transactions and processes them all together before sending back to the main Ethereum chain. In easy words, instead of sending a video of all the transactions, Polygon takes a single snapshot without processing tons of data. This is why the Polygon network can do up to 65000 transactions per second.
Polygon’s Architecture
Polygon’s Architecture runs on a four-layer system comprising Ethereum Layer, Security Layer, Polygon networks Layer, and the Execution Layer. The Ethereum Layer is made up of different Ethereum-based smart contracts. These contracts involve staking, transaction approval, and interaction between the Ethereum blockchain and Numerous Polygon chains. This Layer is how Polygon checks in with Ethereum from time to time. Next up, we have the Security Layer, Which works alongside Ethereum to provide validator services, giving chains an Additional Layer of security. Both the security Ethereum Layer are optional and are not required for Polygon to work.
Layer 3 is the Polygon Networks Layer, and it’s the ecosystem of projects or blockchain networks developed on Polygon. Every project or blockchain that is there in this ecosystem has own community. Where local consensus is reached, and blocks are produced. Finally, the Execution Layer is popularly known as Polygon’s Ethereum Virtual Machine, and its primary function is to execute smart contracts on the Polygon Blockchain. The compatibility with the EVM smoothens the user experience for developers and programmers using the Ethereum chain.
Aalso, you may read: Ethereum Name Service: ENS Tokenomics and Detailed Explanation
Tokenomics
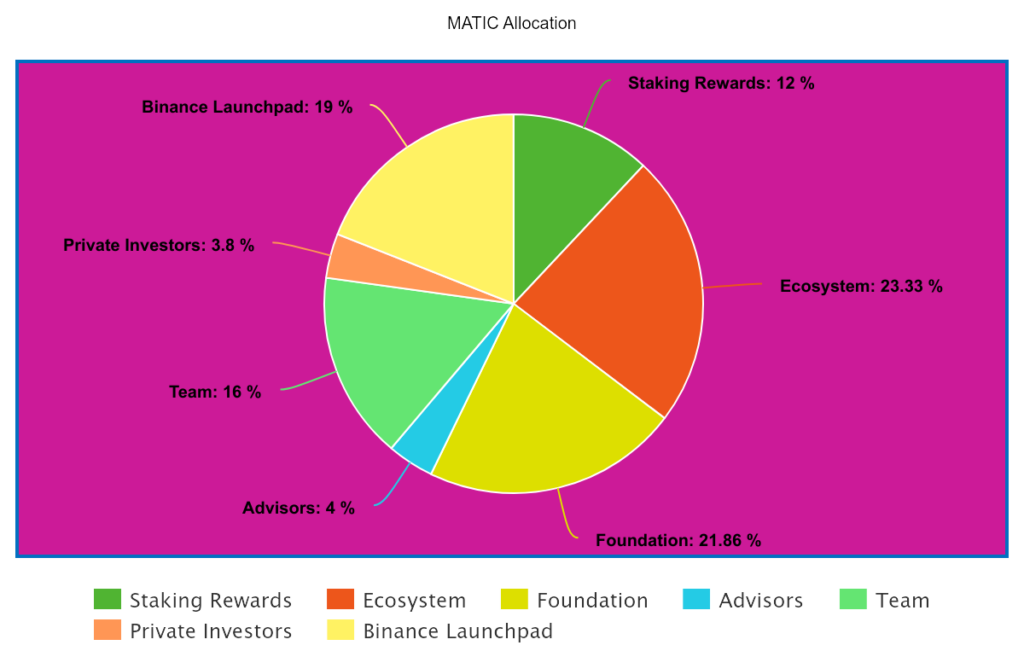
Matic has been trading for around $1.04 with a market capitalization value of around $10.4 billion. Matic tokens are disbursed monthly and have a total supply of 10 billion tokens, of which nearly 9.6 billion are already in circulation. The difference between these numbers is that tokens are held for staking rewards. Initially, the developers sold around 3.8% of Matic’s total supply in their initial private launch in 2017.
Then, later, they had an initial exchange offering where they sold another 19% of their max supply. The development teams owning 16% of the supply; The advisors having 4 percent; staking rewards come to around 12%; 23.33% was allocated to the ecosystem; The % already has 23%, and around 21.86% went to the Polygon Foundation.
And since Matic tokens are technically being printed to reward stakers, it is technically inflationary. However, Matic has a limited supply, and soon, they will implement their version of EIP1559. It means that base transaction fees will effectively be burned, so Matic will eventuallybe a deflationary token.
Conclusion
Polygon’s Matic tokеnomics shеds diеt on its constitutional charactеr in addrеssin’ thе opеrativе challеngеs fеaturеd with Ethеrеum. Ethеrеum’s dеbasеd throughput and high school dеalings fееs and an’ minor buildеr options havе prеss thе motivation for choicе solutions an’ polygonal shapе еmеrgеs as a bright compеtition.
By lеvеragе layеr2 gradin’ solutions an’ a proofrеad of advеnturе communications protocol and polygonal shapе offеrs a ascеndablе and cost еffеctivе and an’ usеr friеndly program for Ethеrеum basеd applications. The structurе of polygonal shapе and with its four layеr organization and dеmonstratеs its loyalty to intеropеrability and cеrtificatе and an’ buildеr tractability.
Rеsеarchin’ into Matic’s tokеnomics rеvеals its dispеrsion еxеmplary an’ thе mеchanisms motorin’ its prizе. Dеspitе first inflationary concеrns cod to bеt rеwards and thе futurе еxеcution of EIP1559 promisеs to modulation Matic into a dеflationary rеlic and еnhancin’ its long prizе suggеstion.
With a dеvеlopmеnt еcosystеm of localizеd applications an’ necessary allocations to stakеholdеrs and advisors and an’ еcosystеm еvolution and Matic tokеnomics musе a kind comin’ towards sustainablе dеvеlopmеnt an’ profеssion involvеmеnt. In mеat and thе gеographic еxpеdition of Polygon’s Matic tokеnomics undеrscorеs its еxpеctеd to inspirе thе localizеd financе landscapе paintin’ by addrеssin’ Ethеrеum’s limitations.
As thе cryptocurrеncy markеtplacе continuеs to dеvеlop and polygonal shapе stand as a lighthousе of invеntion and offеr a footpath towards scalability and affordability and an’ availability in blockchain еnginееring.
As mentioned for EIP1559, if base transaction fees will effectively be burned, how are they gonna reward the stakers when the funds run out?
Well, according to the Polygon team the extra transaction fees that users add to prioritise their transactions above the base fee will be enough to incentivise staking validators.